Following are the main differences between Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and Universal Analytics (GA3).
In this article, we will discuss the key differences between Universal Analytics (GA3) and Google Analytics 4 (GA4). Google Analytics 4 is not an upgrade to Universal Analytics. It is a completely different new version of Google Analytics which works on event-driven based models and also comes with a different set of reports.
Let’s dive deeper to understand what are the differences between GA3 and GA4
#1 Reporting interface

At first glance, the GA4 reporting view may look intimidating as many of the reports and metrics that you have been familiar with are not there. They have either been removed or replaced.
Businesses should not expect to see the same reports that were available in GA3 since GA4 has a different set of reports. You are going to see different sets of reports in your GA4 view and you are not going to see many reports. This is because many of the reports are generated only when you start tracking events.
The reporting interface of the GA4 view looks similar to that of Google Analytics for Firebase (because GA4 is built on Firebase analytics). But it is quite different from any GA3 reporting view.
#2 Measurement model
GA3 (aka Universal Analytics) uses the measurement model which is based on sessions and pageviews. GA3 uses a session-based model to track data, which means analytics collects and stores information like pageviews, events, transactions as hits and every action taken by the user in a given time frame.
Whereas, GA4 uses the measurement model which is based on events and parameters. In GA4 even a ‘pageview’ is considered as an event. This means GA4 uses an event-based model to track data.
Every activity taken by the user in GA4 will be considered as an event and these events will have more detailed information. Let’s say we are tracking ‘pageview’ as an event, this would also have the title of the page, user location, etc.
#3 Tracking IDs
In order to set up any type of tracking in GA4 via GTM, we use the measurement ID.
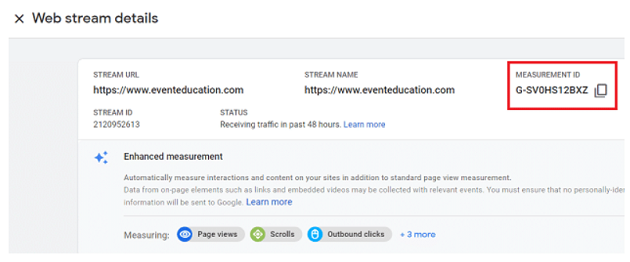
Whereas, in order to set up any type of tracking in GA3 via GTM, we use the tracking ID.
If you have set up a GA4 property with a web data stream, then your measurement ID begins with the characters ‘G-’.
For example G-SV0HS12BXZ
If you have set up a GA3 property then it uses the tracking ID (and not measurement ID) and this tracking ID begins with characters ‘UA-‘.
For example UA-1509844-8
4 View and Data Streams Setup
In GA3 you have an option to create additional views. You can create a view for your app and web tracking separately.
In GA4 you do not have the option to create views. However, you do have an option to create data streams for your web and apps.
#5 Event tracking set up
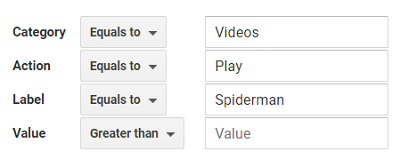
The events are tracked differently in GA4 than in GA3.
When you are using GA3, all the tracked events must follow the category-action-label-value schema:
This is not the case with GA4 which provides much more flexible event tracking setup. In the case of GA4, additional information is supplied to an event tracking via parameters:
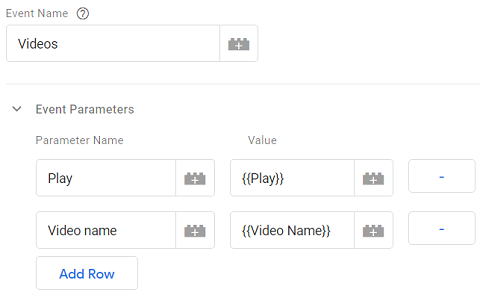
In GA4 you do not have an event category, action and label, but it captures the 4 categories of events, which are
- Automatically collected events
- Enhancement Measurement events
- Recommended events
- Custom events
You can send up to 25 custom parameters per event and each value can be 100 characters long.
There is a limit of 500 unique event names per GA4 property.
#6 Event tracking automation
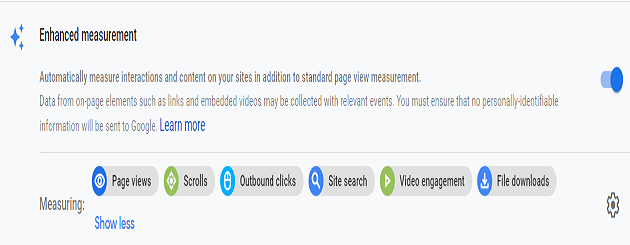
A GA4 property has got the ‘enhanced measurement’ feature built-in which allows automatic tracking for certain types of events (like scroll tracking, video tracking, exit tracking, site search tracking, etc) without any additional coding/tagging.
In automatically collected events, no code changes are required and events will be automatically captured if the page that you are looking to track has gtag.js implemented.
Enhanced measurement tracking gives us the capability to activate extensive event tracking in all marketing channels. Aside from the default events tracking you will also be able to track (app first_open, i.e. opening of the app; in_app_purchase, i.e. shopping through the app) and dedicated events.
Out of the four types of event categories in GA4 automatically collected events and enhancement measurement events do not require any code changes. However, the below two event categories require code changes to the app or web.
- Recommended events
- Custom events
Recommended events have predefined names and parameters and are used for specific business verticals like retail and ecommerce, travel, games, jobs and real estate.
Custom events are implemented by people like you and me. Before creating the custom events always double-check if your event tracking needs can be met from automatically collected events or enhancement events or recommended events.
Go for custom events only if existing event categories don’t support your needs.
This is something not possible with GA3.
#7 User and event data retention
Through the ‘User and event data retention’ feature, you can set the amount of time for which Google Analytics retains user-specific data (i.e. data that is associated with cookies, user identifiers, or advertising identifiers) for an inactive website user, before automatically deleting it.
In the case of GA3, you can set the amount of time setting to 14 months, 26 months, 38 months, 50 months or ‘Do not automatically expire’:
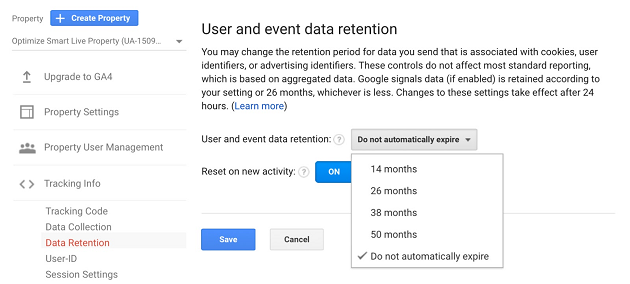
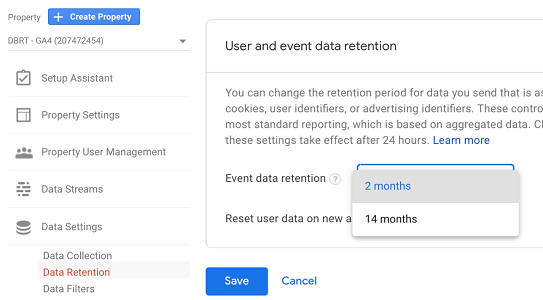
But in the case of GA4, you can set the amount of time setting to either 2 months or 14 months. There are no other options available:
#8 Ecommerce tracking
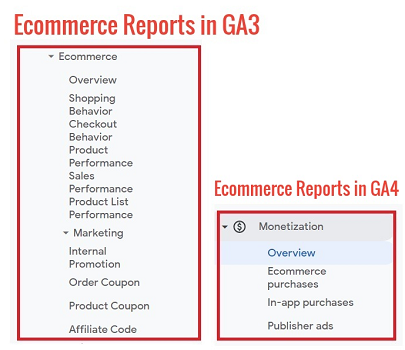
The ecommerce tracking capabilities provided by GA4 are still in their infancy. They are nowhere as powerful as ecommerce tracking capabilities provided by GA3.
Because of this reason alone, GA4 is not yet ready for commercial consumption.
#9 Cross-device and cross-platform tracking
Since GA4 is based on app+web data, it gave marketers a way to track users across apps and websites. This is built with an intent to apply advanced machine learning, which will automatically highlight helpful information for the marketers.
In the case of GA4, both the web and app data use the same schema. Whereas in the case of GA3, this is not the case.
Because of this reason, GA4 provides much more robust and reliable cross-device and cross-platform tracking than GA3.
#10 Attribution modelling
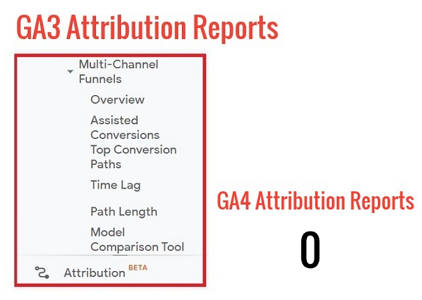
GA3 provides powerful attribution modelling capabilities via multi-channel funnels and attribution reports. Such attribution modelling capabilities do not exist in GA4. This is yet another powerful reason why GA4 is not yet ready for commercial consumption.
#11 Custom dimensions
In GA4, custom dimensions are created differently than in GA3.
You create a new custom dimension in GA4 by creating a new custom event parameter.
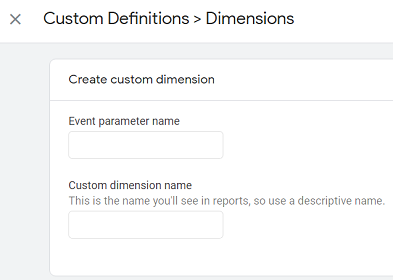
If you are using GA3 then you can set/change the scope of your custom dimension to ‘Hit’, ‘Session’, ‘User’ or ‘Product’.
In the case of GA4, it is not possible to set/change the scope of your custom dimension. A GA4 custom dimension has only one scope and that is ‘hit’ scope.
You can not create a custom dimension with the ‘session’ scope in GA4. However, there are workarounds for creating custom dimensions with ‘user’ or ‘product’ scope.
If you want to create a custom dimension with ‘user’ scope in GA4 then create ‘User properties’.
If you want to create a custom dimension with ‘product’ scope in GA4 then use item parameters (‘item_category’, ‘item_category_2’, ‘item_category_3’ etc).
#12 Custom metrics
In GA4, custom metrics are created differently than in GA3.
You create a new custom metric in GA4 by creating a new custom event parameter and by specifying the unit of measurement.
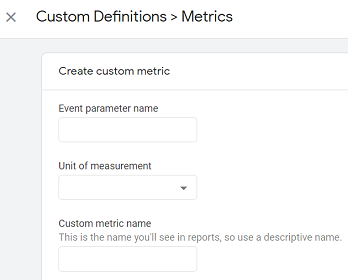
If you are using GA3 then you can set/change the scope of your custom metric to ‘Hit’ or ‘Product’.
In the case of GA4, it is not possible to set/change the scope of your custom metric. A GA4 custom metric has only one scope and that is ‘hit’ scope.
#13 Debugging
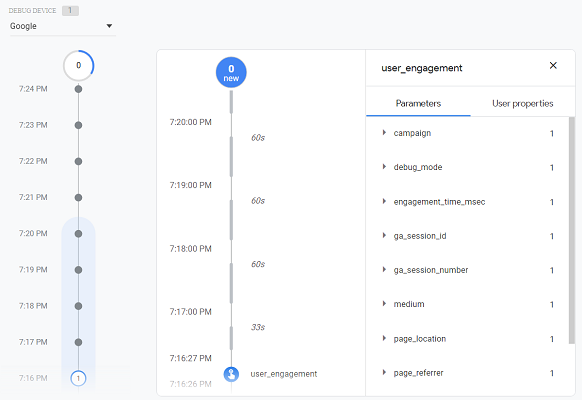
The GA4 reporting view provides the debugView report through which you can validate your analytics configuration from within the reporting interface. This is something not possible with a GA3 reporting view.
#14 Engagement metrics
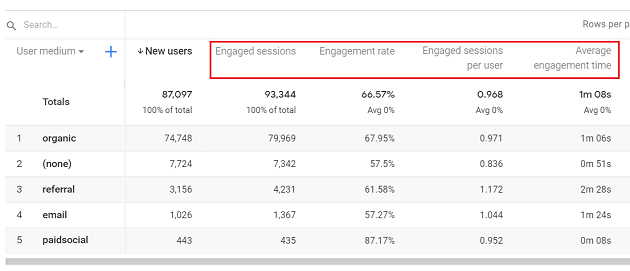
GA4 reporting view provides a new set of engagement metrics (Engaged Sessions, Engagement Rate, Engaged Sessions per User, Engagement Time) which can much more accurately track users engagement with your website/app than the pageviews and bounce rate metrics used by GA3.
Note: There is no concept of bounce rate in GA4.
#15 IP anonymization
Under GDPR, an IP address is considered as personal data.
Google Analytics tracks and stores the IP addresses of your website users in order to report on geolocation data. However, GA does not report on IP addresses in its reports.
If your privacy policy or local privacy laws prevent the storage of full IP addresses then you can use the IP anonymization feature to anonymize/mask website visitors’ IPs.
When you anonymize visitor IP, the last three digits from your website visitor’s IP address are automatically dropped/deleted.
In other words, the IP anonymization feature sets the last octet of IPv4 user IP addresses and the last 80 bits of IPv6 addresses to zeros.
For example, if a website visitor has a public IP of 12.214.31.144 then as soon as the IP data is received by the Analytics Collection Network, Google will anonymize/mask the IP to 12.214.31.0
If you are using the GA3 property then you have the option to enable or disable IP anonymization.
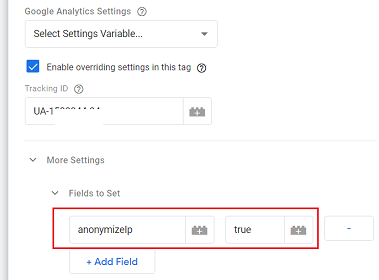
The IP anonymization is disabled by default in GA3.
However, if you are using a GA4 property then the IP anonymization feature is built-in, is enabled by default and you can not disable it.
#16 Reporting views
If you are using GA3, you can create up to 25 reporting views per property. But in the case of GA4, you can use only one reporting view.
Currently, there is no option to create additional views in GA4.
However, there are workarounds available. You can create new ‘Audiences’ or ‘Data Streams’ and use them in place of filtered views.
#17 BigQuery
GA4 comes with a free connection to BigQuery. So you can access the raw GA4 data and can run SQL queries on it. This helps in more precise and multilevel data analysis of your users so that it is easy to understand the user activities on the website.
In the case of GA3, only GA 360 customers can use this feature.
#18 Advanced analysis reports
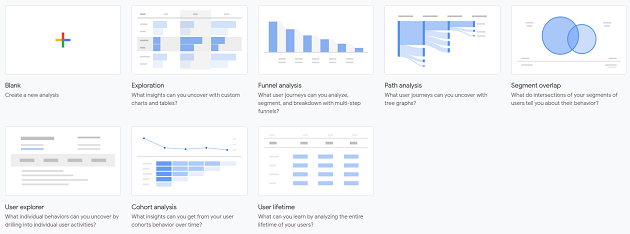
The reporting view of the GA4 property comes with a new set of reports called ‘Analysis’ which let you do advanced analysis.
The users who have already used Firebase for mobile tracking will be quite familiar with the new Google Analytics 4 UI as the GA4 UI is similar to the Google Analytics for Firebase UI.
With the advanced analysis, you will be able to understand the customer journey in both mobile and web over the different marketing channels. Apart from this you also have plenty of options with GA4 like custom funnels and analyze the potential segments overlapping to make uniformed decisions.
Following are the various advanced analysis reports:
- Exploration report
- Funnel Analysis report
- Path Analysis report
- Segment Overlap report
- User Explorer report
- Cohort Analysis report
- User Lifetime report
In the case of GA3, only GA 360 customers can use this feature.